CALIFORNIA SEA LION
Zalophus californianus

LENGTH
2,4 m
WEIGHT

300 kg
LIFESPAN

22 years
The California sea lion is a species of pinniped mammal of the otariid family that lives off the northern Pacific coast.
General characteristics
Sea lions are sexually dimorphic; males are larger and heavier, weighing between 300-380 kg and measuring about 2.4m in length, while females generally weigh no more than 100kg and are 2m long. In addition, males have a pronounced sagittal crest.
They have a hydrodynamic body, with a layer of fat underneath the skin, to provide warmth and buoyancy. The pelage is dark brown, although it may be temporarily light grey or silver after moulting.
They have colour vision, although it is limited to the blue-green area of the colour spectrum. Their large eyes help them compensate for low light levels in the underwater environment, while their whiskers (also called vibrissae) enhance their sense of touch and allow them to detect vibrations underwater.
Sea lions are very similar to seals. They can be distinguished by these three points:
- Sea lions have small pointed ears, while seals have no ears, but instead have two holes on their heads.
- Sea lions use their four flippers for support and allow them to walk or even run. Seals glide, dragging their bellies on the surface.
- And finally, sea lions have claws on each hind flipper while seals do not.
Feeding
These animals feed on a wide variety of marine foods, including fish, molluscs and squid. They do not chew their food, but swallow it whole. They only use their teeth to capture fish and to defend themselves against predators.
Behaviour
California sea lions are extremely gregarious and form large aggregations when on land. Individuals lie close to each other, or even on top of each other. They sleep on top of rocks to ward off predators.
They are very sociable and can be found in large groups, on cliffs, coasts and even on docks and shipping bollards.
The communication is done through a variety of vocalisations but the most commonly used is their characteristic bark. Territorial males are the loudest and most continuous callers, and barking occurs constantly during the peak of the breeding season.
Reproduction
During the breeding season, males establish territories on beaches and aggressively defend their females against other males.
The breeding season takes place between May and July. Females usually give birth to one calf each year, which weighs about 6kg at birth. Gestation lasts between 7 and 10 months.
The calves feed on their mother’s milk from birth until they are 12 months old, but the exact period depends on the individual mother and calf.
Threats
California sea lions face threats such as poaching, entanglement in fish waste and pollutants, which can affect the animals’ immune systems and general health.
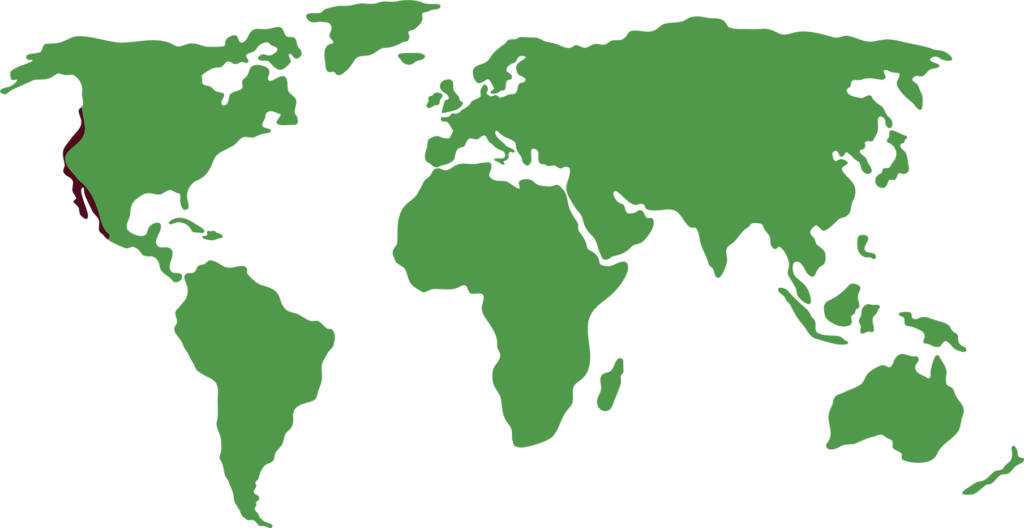
Distribution
They are distributed along the North Pacific coast of America, from southern British Columbia (Canada) to western Mexico, including Baja California.
Did you know?
Most of their water intake comes directly from the fish they eat, although they may occasionally drink small amounts of seawater.
They are called sea lions because they produce loud roars like lions. In addition, in some species, the males develop a lot of hair around their necks, similar to a lion’s mane.
They can stay underwater for an average of 8 to 20 minutes and at a depth of between 135 and 272 metres.
Conservation status