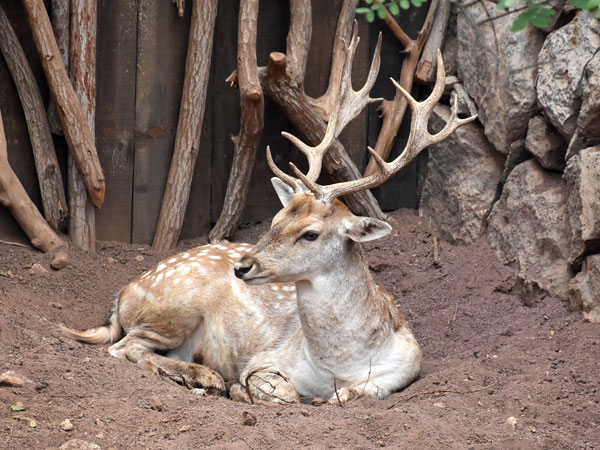
EUROPEAN FALLOW DEER
Dama dama

LENGTH
155 cm
WEIGHT

80 kg
LIFESPAN

25 years
The European fallow deer is a species of ruminant mammal belonging to the Cervidae family. It is known for its agility and speed.
General characteristics
The fallow deer has an elegant, slender body with slender, strong legs. Its coat is reddish brown with black and white spots all over the body, and its belly is white.
Males have branched horns that can reach more than 50 cm in length and have a distinctive “V” shaped appearance. The horns shed and regrow each year, and their size and branching increase with the age and health of the animal.
Fallow deer have dark eyes and long, movable ears that allow them to detect potential dangers and predators. Their excellent sense of smell and hearing also contribute to this cause.
Feeding
It is a herbivorous animal that feeds mainly on fresh grasses and herbs. In autumn, when grasses and herbs begin to dry out, they feed on leaves of shrubs and trees, fruits and ripe berries. And when most plants are inaccessible, they turn to tree branches and bark.
Behaviour
This species is very socially united. They stay together in groups that are generally divided into two flocks: females with fawns and males. The two genders mix freely in groups to socialize in open areas, although at other times they only come together during the breeding season.
They are crepuscular and nocturnal animals, which means they are most active at dawn and dusk. During the day, they usually rest and ruminate in shaded and protected areas.
Males are usually territorial and establish their territory by defending an area where there is an abundance of food and water.
Reproduction
They are polygamous. Male fallow deer challenge each other in a show of strength to get the female. The gestation period lasts approximately 8 months and in spring, the female will give birth to a single fawn. The young can walk soon after birth, but for safety, they remain hidden for several weeks until they are stronger.
Threats
Fallow deer are prey to humans and large predators such as wolves, cougars and bears.
Since the 19th century, a serious decline in populations has been observed and they have disappeared from almost all regions where they were formerly found. Today, there are various programs for the protection of fallow deer and they are quite common in introduced areas.
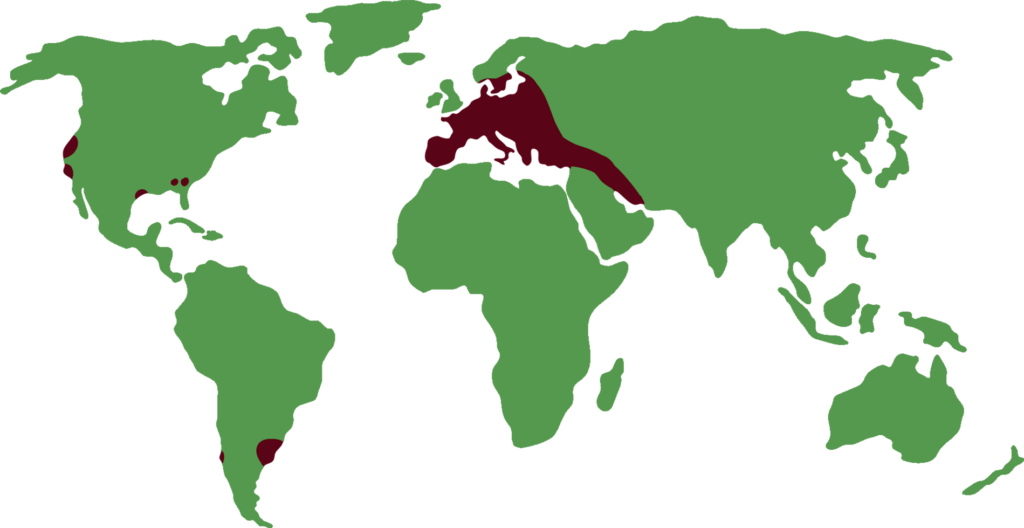
Distribution
The European fallow deer is found throughout much of Europe, from Spain to Russia. Introduced populations have also been established in South America, New Zealand, Australia and South Africa.
Did you know?
They are capable of jumping up to 2 meters high and 6 meters long.
They can run at speeds of up to 56km/h to escape predators.
In winter the white spots on the back disappear as the coat becomes darker and slightly grayish.
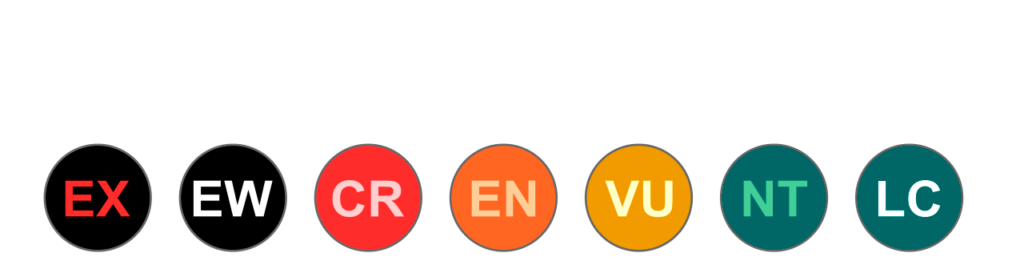
Conservation status