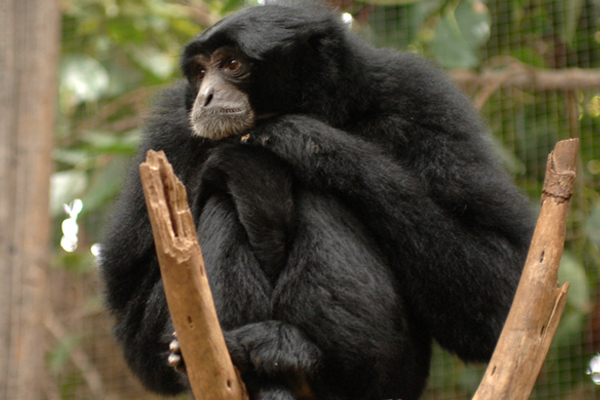
GIBBON SIAMANG
Symphalangus syndactylus

LENGTH
1 m
WEIGHT

13 kg
LIFESPAN

30 years
The Siamang Gibbon is a species of hominoid primate of the family Hylobatidae. It is the largest of the lesser apes, and can be almost twice as large as other gibbons.
General characteristics
The Siamang Gibbon has two unique characteristics. Firstly, it has two toes on each foot (the second and third toes) that are partially joined by a membrane, hence the specific name syndactylus.
Secondly, it has a large gular sac that can inflate to the size of its head. The gular sac allows it to emit very characteristic powerful sounds.
Its black fur is long and dense. The body is slender, the arms being longer than the legs. It has very light bones, which enables it to perform spectacular swinging movements high up in the forest.
Feeding
It feeds mainly on various types of plants, flowers and fruits, although it may also occasionally consume insects.
Behaviour
Siamang gibbons are a very social primate species and exhibit a variety of tactile and visual gestures, along with actions and facial expressions to communicate and enhance social bonds within their family group.
In the morning, they spend their time in feeding, moving, foraging and social activities. When midday arrives, they take a break to groom each other or to play. The rest of the day is spent resting on the branch of a large tree, lying on their backs or stomachs. Grooming is also one of the most important social interactions between family members.
They are territorial and interact with other family groups by making loud calls to let other groups know where their territory is.
Reproduction
The siamang gibbon is one of the few primates that mate for life, with the pair and two or more offspring making up the group.
Gestation period lasts between 7 and 8 months and gives birth to a single calf. The mother cares for the calf for the first year of its life and the father also assumes an important role in its care.
Threats
This species is threatened by the destruction of its habitat (conversion of the forest into plantations) and illegal animal trafficking.
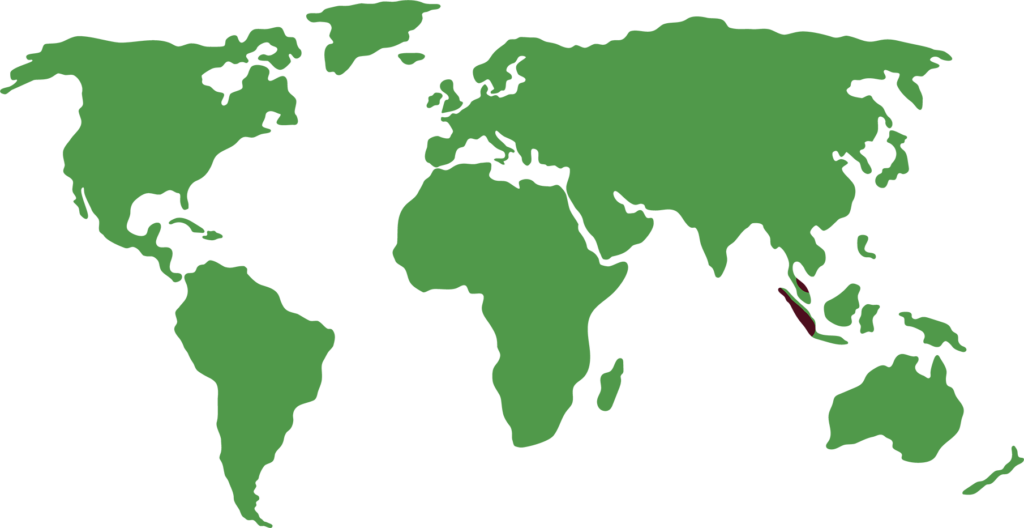
Distribution
It is native to the forests of Malaysia, Thailand and Sumatra. It lives in both lowland and montane forests (including rainforests) and can be found at altitudes up to 3800 metres.
Did you know?
As a frugivorous animal, the siamang disperses seeds by defecation as it travels through its territory and contributes to forest regeneration.
Siamang females are very protective of their young, so poachers often kill the mothers first to keep the young.
They start their morning songs just before dawn and can last up to 30 minutes.
Conservation status